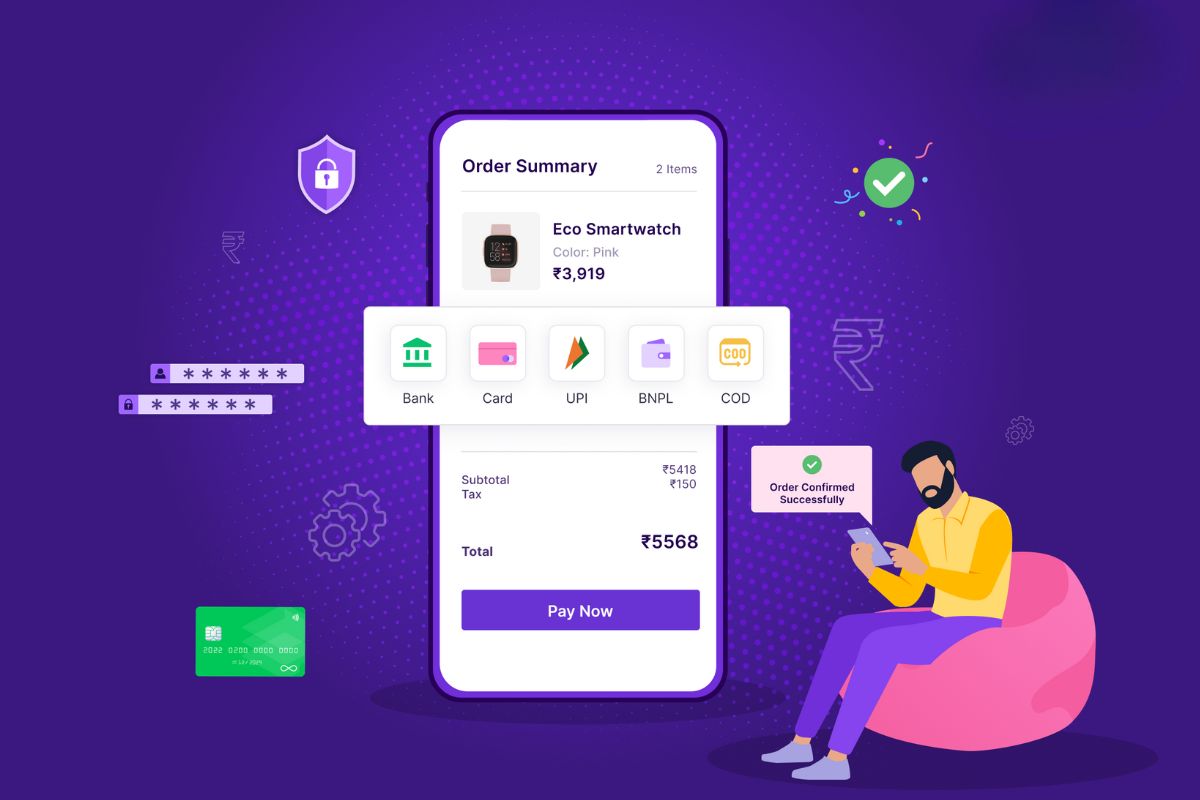
The payment journey matters in modern U.S. commerce, from independent online shops to enterprise e‑commerce platforms. Behind every successful sale is an infrastructure that secures, verifies, and finalizes the customer’s payment, and at its center sits the payment gateway. While shoppers expect frictionless checkouts, businesses rely on gateways to encrypt card data, interface with banks, and detect fraud. In the American market, where speed and security are as critical as trust, the gateway method becomes a silent partner in each purchase. This article draws on insights and explains what a payment gateway is, how it performs its essential role, and why it is indispensable in U.S. online payments.
✦ What Is a Payment Gateway?
It is a digital platform that acts as an intermediary between a merchant’s website or app and the financial institutions involved in payment processing. It captures the customer’s payment data, whether credit card details, digital wallet credentials, or other forms of payment, and securely transmits this information to the acquiring bank or payment processor. JPMorgan describes the gateway as the central link connecting customers, merchants, and banks in a manner that ensures both security and real-time authorisation.
✦ Broader Role in Digital Commerce
Beyond simply forwarding data, a gateway payment handles encryption using SSL/TLS or OAuth protocols (as noted by Stripe and J.P. Morgan), conducts fraud checks with CVV/AVS verification, and offers reporting tools that provide merchants with transaction history, refund tracking, and analytics. The gateway ensures sensitive customer data is never exposed while payment is authorised and transmitted confidently.

➝ How Does It Work?
Although it feels instantaneous, a lot happens in the few seconds between clicking “Submit Payment” and receiving a confirmation. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
1. Customer Initiates Payment
The process begins the moment a customer decides to make a purchase. They select the desired items and check out on the website or app. At this stage, the customer is prompted to enter their payment details, typically credit or debit card information such as the 16-digit card number, CVV (Card Verification Value), expiration date, and billing address. Once this information is filled in, the user clicks the “Pay” or “Submit Payment” button. Although it might appear as a single step, this action sets off a complex series of backend processes to securely verify and process the payment.
2. Data Encryption
Once the payment details are submitted, the payment gateway encrypts sensitive information immediately. Encryption transforms the readable card data into a secure code using advanced encryption protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security). This prevents unauthorized access or interception during transmission across networks. Encryption plays a crucial role in maintaining trust in online payments by ensuring that personal and financial data is protected from cyber threats.
3. Authorization Request
After encryption, the gateway sends the data to the payment processor. The processor acts as a middleman, forwarding the information to the issuing bank, that is, the bank or financial institution that issued the customer’s card. This is where the authorization process begins. The issuing bank receives the encrypted data and initiates a real-time check to validate the card and assess whether the transaction can proceed. The entire exchange between these systems happens almost instantaneously and is powered by advanced fintech infrastructure.

4. Approval or Decline
The issuing bank now evaluates the request based on several criteria. It checks whether the card number is valid, if the card is active, whether the customer has sufficient funds or credit, and if there are any suspicious or potentially fraudulent patterns. If everything checks out, the bank approves the transaction and sends a message back through the same route, from bank to processor, then back to the payment gateway. If any of the checks fail, the bank sends a decline message. The process takes a few seconds but involves multiple security checks and validation layers.
5. Notification and Completion
The payment gateway receives the response and immediately notifies the merchant. If the transaction is approved, the customer is shown a confirmation screen or receipt, and the merchant can proceed to fulfill the order. The user is informed via an error message if the payment is declined. They are typically given options to retry the payment, double-check their information, or choose an alternative method like another card or digital wallet. This step ensures a smooth user experience and reduces cart abandonment due to failed payments.
6. Settlement
Once a transaction is approved, the final step is the funds settlement. This involves transferring money from the customer’s bank (or credit issuer) to the merchant’s acquiring bank. While the payment confirmation to the user is almost immediate, the actual funds transfer typically takes 1–2 business days to complete. The acquiring bank eventually credits the merchant’s account with the transaction amount, minus any processing or gateway fees. This behind-the-scenes step ensures that merchants receive their earnings promptly and reliably.
✦ Examples and Importance of Payment Gateways
There are dozens of payment gateway providers in the U.S., but a few names consistently stand out for their innovation, reliability, and user experience.
➝ Notable U.S. Payment Gateways
- Stripe: Known for its developer-friendly tools and seamless integration, Stripe allows U.S. businesses to accept credit cards, ACH transfers, Apple Pay, and more. Startups and large tech companies widely use it.
- Shopify Payments: This is a built-in gateway for Shopify merchants. It removes the need for third-party gateways, supporting all major cards, Shop Pay, and digital wallets.
- Authorize.Net: One of the earliest players in the industry, it’s known for its fraud protection features and support for recurring billing.
- Square: While it began with in-person POS systems, Square also offers a robust online payment gateway for U.S. retailers and service providers.
✦ Why It Matters?
A payment gateway does more than move money; it shapes your brand’s credibility. In the U.S., consumers are susceptible to how safe and professional a checkout feels. Many will abandon their cart if the payment experience is clunky or slow.
According to BigCommerce, nearly 70% of online shoppers in the U.S. have abandoned a cart due to friction in the checkout process, often tied directly to poor payment experiences. That’s where a good gateway changes the game.
➝ Gateways also play a critical role in:
1. Fraud prevention:
Through CVV checks, address verification, tokenization, and AI-driven fraud filters.
2. Speed and reliability:
Instant approvals mean faster sales and better customer satisfaction.
3. Global reach:
Many gateways now support multiple currencies and local payment methods, allowing U.S. businesses to expand abroad.

4. Recurring billing and subscriptions:
Gateways enable automatic billing cycles without manual input for SaaS companies or subscription box services.
✦ How Does Online Payment Work?
Let’s walk through a real-world example of how online payments flow through a payment gateway in the U.S.
✦ The Scenario
A customer visits an online store to buy a $50 T-shirt. They add it to their cart, enter shipping information, and check out.
➝ Step-by-Step Process
1. The Checkout Page:
They enter their credit card information on a secure form. The page is SSL-protected, and the payment gateway is embedded behind the scenes.
2. Data Transmission:
The gateway encrypts their card details and sends them to the payment processor.
3. Card Verification:
The processor forwards the data to the issuing bank, which checks if the card is valid and has enough funds.

4. Authorization:
The bank approves the transaction and sends a “Yes” message back to the gateway.
5. Confirmation:
The merchant’s site displays a success message, confirming the order.
6. Settlement:
The funds are transferred into the merchant’s account in one to two business days.
From the customer’s perspective, it’s just a few clicks. However, the payment gateway works hard to ensure everything is fast, encrypted, and fraud-free.
Shopify emphasizes that integrating the right gateway reduces technical complexity, eliminates errors during checkout, and builds customer loyalty through trust and speed.
Conclusion
The payment gateway is the foundation of digital trust. In the U.S. market, where consumers are tech-savvy and privacy-conscious, businesses can’t afford to treat payments as an afterthought. From encryption and fraud prevention to offering flexible payment options and detailed analytics, a good gateway does more than just process money. It improves customer experience, boosts conversion rates, and supports long-term growth. Choosing the right gateway depends on your business model, platform, and customer preferences.