In recent years, blockchain has moved from being a buzzword in tech meetups to a foundational piece of modern digital infrastructure. Yet, ask the average person what blockchain technology is, and you’ll likely get an answer centered around Bitcoin, or worse, complete confusion.
However, blockchain is more than just the engine behind cryptocurrencies. It’s a powerful innovation that promises greater transparency, security, and efficiency across countless industries. From digital contracts to supply chain systems, secure identity management, and decentralized finance, blockchain is reshaping how we record, validate, and exchange information.
So, let’s understand blockchain technology, why it matters, and how it’s being used to solve real-world problems in simple, digestible terms.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a shared digital ledger. Think of it as a record book not stored in one place but distributed across a network of computers, known as nodes. Every transaction or data entered into this ledger is grouped into blocks. These blocks are linked chronologically, forming an unbreakable chain called a blockchain.
What makes blockchain special is that it’s nearly impossible to alter once information is added to the chain. This immutability, combined with decentralized control, eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries like banks or centralized authorities.
So, when people ask what blockchain technology is, the most accurate answer is that it’s a decentralized system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult, or impossible, to change, cheat, or hack.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Databases
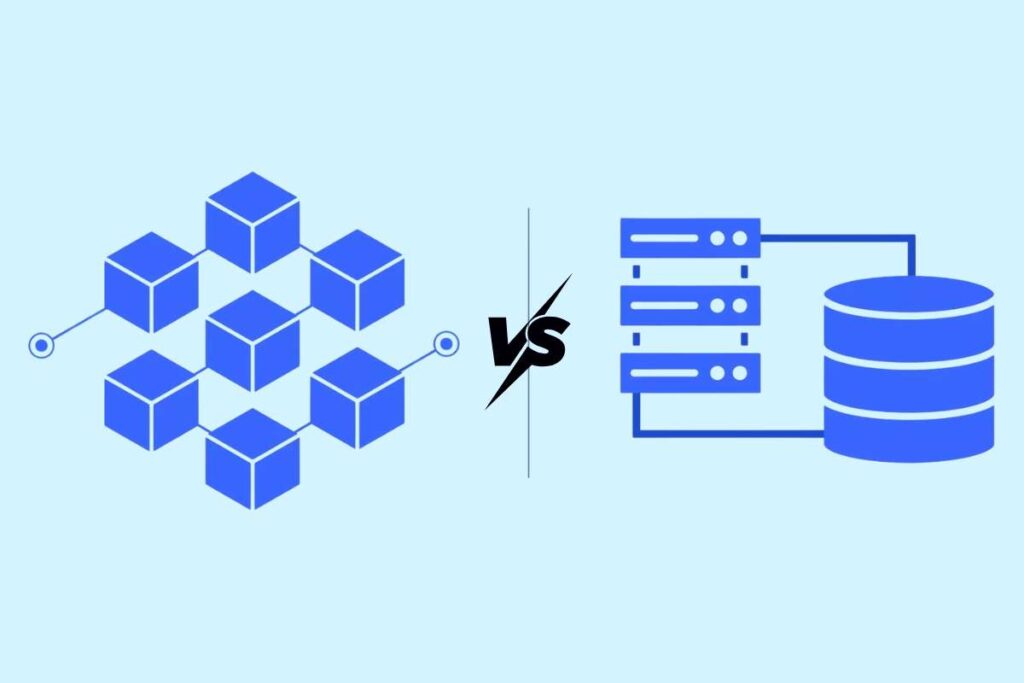
In a traditional database, a single organization owns and controls the data. They decide what gets added, who has access, and how the information is updated. While efficient, this setup makes the system vulnerable to data breaches, corruption, or manipulation.
Blockchain takes a different approach. Since all nodes in the network hold identical copies of the ledger and must validate each new transaction through consensus mechanisms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake), tampering with records without being caught becomes almost impossible.
That’s a key reason industries across finance, healthcare, logistics, and government are exploring blockchain as a safer, more transparent alternative.
How Blockchain Works
To understand what blockchain technology is in practical terms, let’s look at a basic transaction process:
- A user initiates a transaction, such as transferring funds or submitting data.
- The transaction is shared across the peer-to-peer network.
- The network validates the transaction using an agreed-upon consensus protocol.
- A block is formed that contains the transaction data, a timestamp, and a unique code called a hash.
- The block is linked to the previous block, creating a secure chain.
- The updated chain is shared with all participants in the network.
Because each block contains information from the block before it, any attempt to alter a single record would require re-mining every block after it, an almost impossible task without majority control over the network.
The Key Features of Blockchain Technology
To grasp what blockchain technology is, we need to highlight the core qualities that make it stand out:
- Decentralization: No single entity has control. Instead, the ledger is maintained by multiple nodes in the network.
- Transparency: All participants can view the ledger. Transactions are visible and traceable.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed without consensus.
- Security: Advanced cryptography secures each block and verifies transactions.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These rules ensure that all nodes agree on the current state of the ledger, preventing fraud or duplication.
These features build trust in systems where users don’t necessarily trust each other, an invaluable concept in today’s digital world.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Many people limit their understanding of blockchain technology to cryptocurrency. While digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum are high-profile use cases, blockchain is widely used, often behind the scenes.
1. Supply Chain Transparency

Companies like IBM and Walmart use blockchain to track food products from farm to shelf. Every step, from harvesting to shipping to delivery, is recorded on a blockchain, making recalls faster and fraud detection easier.
2. Financial Services
Blockchain allows faster, cheaper cross-border payments, reduces settlement times in stock trading, and opens new doors for decentralized finance (DeFi). Institutions like JPMorgan and HSBC are developing blockchain-based settlement networks.
3. Healthcare
Patient records stored on a blockchain can be securely shared across providers without compromising privacy. This ensures better coordination, reduces redundancy, and puts patients in control of their health data.
4. Smart Contracts
These self-executing contracts coded on a blockchain automatically trigger when conditions are met. Think of it as digital legal agreements, with no lawyers or paperwork required.
5. Digital Identity
Blockchain gives individuals secure, portable digital IDs that are hard to forge, which is especially valuable in regions with limited access to government services.
The growing list of applications further expands the answer to blockchain technology; it’s not just a technical tool but a structural innovation.

Challenges That Still Exist
Despite its promise, blockchain isn’t flawless. Scalability remains an issue; most public blockchains can’t handle high transaction volumes quickly. Bitcoin, for instance, processes far fewer transactions per second than Visa.
Energy consumption is another concern, especially in blockchains using Proof of Work (like Bitcoin), which require vast computing power. Efforts are underway to shift toward more sustainable models like Proof of Stake, significantly reducing energy use.
Finally, regulatory clarity is still evolving. Governments worldwide are trying to define legal frameworks for blockchain applications, particularly around crypto-assets and data privacy.
So, when asking what blockchain technology is today, it’s equally important to look at what it could be tomorrow and how we overcome current limitations to unlock its full potential.
The Business Impact: Why Corporates Are Taking Notice
Major enterprises are no longer asking about blockchain technology but are acting on it.
- IBM’s Blockchain Platform is used in food traceability, trade finance, and identity verification.
- PwC notes that blockchain could boost global GDP by $1.76 trillion by 2030, primarily through greater efficiency and trust.
- Governments, including Estonia and the United Arab Emirates, have built national services like digital voting and public record systems on blockchain.
What’s Next for Blockchain?
If the internet revolutionized how we share information, blockchain is revolutionizing how we share value and verify trust. From the rise of tokenized assets to the evolution of Web3 platforms, blockchain’s role is only growing.
Yet, widespread adoption depends on overcoming usability hurdles. For blockchain to reach mainstream users, it needs simpler interfaces, tighter regulation, and more education. People shouldn’t need to understand cryptographic hash functions to use blockchain more than to understand TCP/IP to use the internet.
In the future, the phrase what is blockchain technology may become obsolete, not because it stops being relevant, but because it becomes so embedded in our lives that we no longer question it.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a paradigm shift in how we structure trust. It removes the need for centralized control, replaces it with consensus and transparency, and offers a secure, tamper-resistant way to store data.
So, what is blockchain technology? It’s the architecture for a more open, secure, decentralized digital future. Whether you’re a developer, a business leader, or just a curious mind, now is the time to understand it because blockchain isn’t just coming. It’s already here.


















