In 2025, global corporate financing activity, including mergers, acquisitions, and equity deals, is expected to exceed $12.5 trillion, a 9% jump from last year. From Tesla’s $10 billion stock sale to Microsoft’s $68.7 billion acquisition of Activision Blizzard, every major business move begins with one critical principle: Corporate Finance.
So, what is corporate finance, and why does it matter so much?
Simply put, corporate finance is the financial backbone of every company. It guides how organizations raise funds, manage investments, and create long-term value for shareholders. Whether it’s a startup seeking seed funding or a Fortune 500 firm planning global expansion, corporate finance ensures money works strategically, not emotionally.
In a world where inflation hovers around 5.6% and economic volatility is the new normal, over 70% of CFOs now prioritize capital allocation and liquidity management (Deloitte, 2025). That’s because smart financial planning isn’t just about growth, it’s about survival.
In this blog, we’ll dive deeper into what corporate finance is, explore its key components, functions, and modern trends, and understand why mastering it is essential for every future-ready business leader.
Understanding the Core of Corporate Finance
At its core, corporate finance is the discipline that governs how a company manages its money to achieve long-term growth and profitability. It focuses on three main goals: raising capital efficiently, investing wisely, and maximizing shareholder value.
According to Investopedia, corporate finance deals with all financial activities that businesses undertake, including funding decisions, capital structuring, dividend policies, and investment analysis. In simple terms, it’s about making sure every rupee, dollar, or euro invested in a business generates measurable returns.
But what is corporate finance beyond theory? It’s the framework behind every strategic decision, from how Amazon funds its data centers to how startups like SpaceX secure billions in private funding. Every successful enterprise applies corporate finance principles to balance risk, liquidity, and profitability in a fast-changing global market.
Corporate finance also bridges short-term financial management and long-term strategic planning. For instance, while working capital management ensures a company can meet its immediate obligations, long-term financial strategies such as mergers, acquisitions, or IPOs shape its future growth trajectory.
In essence, corporate finance isn’t just about managing money; it’s about managing vision. It transforms financial data into decisions that fuel innovation, strengthen resilience, and create enduring enterprise value.
Breaking Down the 4 Core Pillars of Corporate Finance

To truly understand what corporate finance is, it’s essential to break down its three fundamental pillars: capital budgeting, capital structure, and working capital management. These components form the foundation of every financial decision a company makes, from funding innovation to sustaining day-to-day operations.
1. Capital Budgeting (Investment Decisions)
Capital budgeting is the process of deciding where a company should invest its money for the best long-term return. It involves analyzing potential projects such as expanding production facilities, acquiring new technology, or launching new products, and determining which ones will create the most value.
Tools like Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period help financial managers make data-driven choices. For instance, Apple’s continuous investment in R&D, which exceeded $34.55 billion in 2024, reflects sound capital budgeting aimed at innovation-led growth.
Effective capital budgeting helps companies balance risk and reward, ensuring that every major investment aligns with long-term strategic goals.
2. Capital Structure (Financing Decisions)
Capital structure defines how a company finances its operations and growth, typically through a mix of debt and equity. The right structure minimizes the cost of capital while maintaining financial flexibility.
For example, Tesla strategically raised equity during its rapid growth phase to avoid high debt burdens, while established corporations like ExxonMobil rely more heavily on long-term debt for expansion.
An optimized capital structure supports stability and shareholder confidence. It ensures that companies can seize growth opportunities without overleveraging or diluting ownership.
3. Working Capital Management (Liquidity Decisions)
Working capital management focuses on managing short-term assets and liabilities, ensuring the business has enough liquidity to meet daily operational needs. It involves balancing inventory, receivables, and payables to maintain cash flow.
According to PwC’s Global Working Capital Report 2024, companies with efficient working capital practices generated up to 25% more free cash flow than their peers. More than €1.56 trillion of excess working capital globally. That extra liquidity often becomes a lifeline during economic slowdowns or market disruptions.
4. Dividend Policy (Profit Distribution Decisions)
A company’s dividend policy determines how much profit is distributed to shareholders versus reinvested in the business. This decision directly affects investor sentiment and market valuation.
For instance, firms like Microsoft consistently pay dividends to reward long-term investors, while fast-growing companies like Amazon reinvest profits into expansion.
The right dividend strategy signals financial health, confidence, and commitment to sustainable growth, all core outcomes of strong corporate finance management.
Ultimately, what corporate finance is can also be seen in how companies manage this balance between rewarding investors and fueling future expansion.
How Corporate Finance Powers Business Decisions?
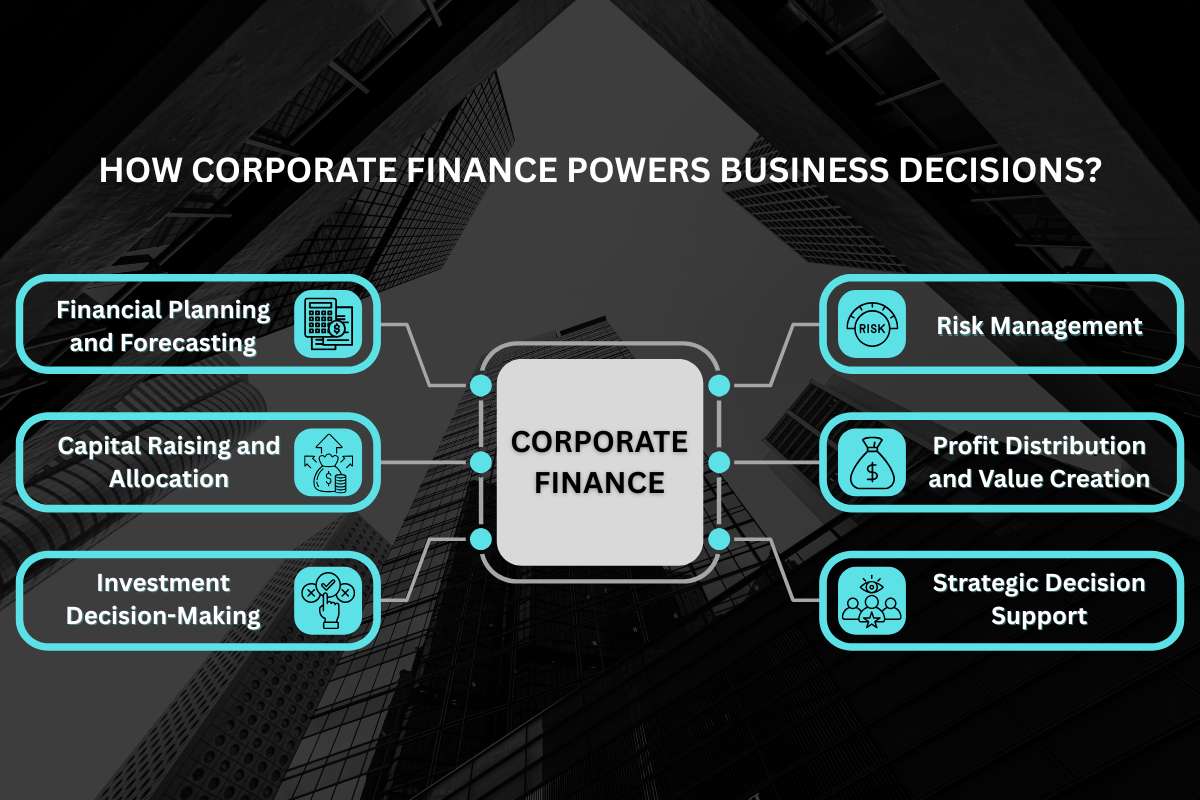
Now that we understand the key components, let’s explore the core functions of corporate finance, the practical actions that bring those components to life. These functions guide how a company plans its finances, raises capital, invests resources, and manages risk to sustain profitability and long-term value creation.
In essence, understanding these functions is vital to answering what corporate finance is and how it operates in the real business world.
1. Financial Planning and Forecasting
Every successful organization begins with a sound financial plan. Corporate finance teams develop forecasts, budgets, and financial models to predict revenue, expenses, and future capital needs.
For example, according to Deloitte’s 2025 CFO Survey, over 68% of financial leaders say data-driven forecasting is now their top strategic priority. This shift shows how corporate finance has evolved from number crunching to long-term strategic planning.
Effective planning ensures that companies not only meet short-term liquidity needs but also have the financial strength to execute growth initiatives confidently.
2. Capital Raising and Allocation
Another key function of corporate finance is determining how to raise and allocate funds. Alphabet’s bond offerings for clean energy projects showcase how efficient capital allocation fuels sustainability and innovation.
For instance, Google’s parent company, Alphabet, raised billions through bond offerings to finance clean energy projects and cloud expansion, balancing low-cost debt with strategic investment.
Corporate finance ensures that the capital raised is directed toward projects that generate the highest return, fueling sustainable growth.
3. Investment Decision-Making
Investment appraisal is where strategy meets execution. Corporate finance teams evaluate potential investments based on their risks, costs, and expected returns.
Tools like discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis and cost-benefit studies guide these decisions. For example, when Meta (Facebook) invested billions in the metaverse, it relied heavily on capital budgeting models to assess the long-term payoff of its innovation strategy.
In short, investment decisions are at the heart of what corporate finance is, converting financial insights into actions that build value.
4. Risk Management
No financial decision is risk-free. That’s why corporate finance functions also include identifying and mitigating financial risks such as interest rate volatility, currency fluctuations, or credit exposure.
Risk management, a vital part of what is corporate finance, protects companies from interest rate, credit, and currency risks. PwC’s 2025 survey shows that 79% of CFOs now treat risk management as a board-level function.
Proactive risk management keeps companies resilient amid market uncertainty, ensuring long-term financial health.
5. Profit Distribution and Value Creation
Corporate finance doesn’t end with earning profits; it’s also about deciding how to distribute or reinvest them. Dividends, share buybacks, and reinvestment strategies all fall under this function.
A company like Apple, which returned over $110 billion to shareholders in 2024 through dividends and buybacks, exemplifies how strategic profit distribution can enhance investor trust and boost stock performance.
Ultimately, the goal of corporate finance is simple yet powerful: to maximize shareholder value while ensuring financial sustainability.
6. Strategic Decision Support
Modern corporate finance extends far beyond accounting. It acts as a strategic partner to leadership, guiding decisions on mergers, acquisitions, sustainability initiatives, and digital transformation.
In a world where capital allocation drives innovation, corporate finance teams play a pivotal role in turning financial insight into competitive advantage.
In summary, the functions of corporate finance ensure that every decision from planning to profit distribution is rooted in strategy, data, and foresight. They form the operational core of what is corporate finance, bridging financial discipline with visionary growth.
How Corporate Finance Differs from Investment Banking (and Why It Matters)?

Many people often mix up Corporate Finance and Investment Banking, but they actually do very different things, even though both deal with money, growth, and business decisions. Think of them as two sides of the same financial coin: one manages a company’s money internally, while the other helps it raise money from the outside world.
Corporate Finance is all about how a company uses its money to run and grow. It deals with day-to-day decisions like:
- How much to invest in new projects?
- Whether to borrow money or use company profits for expansion
- How to keep profits growing steadily over time?
For example, when Tesla decides to invest billions in new battery plants or expand its gigafactories, that’s corporate finance in action, deciding where and how to spend money wisely.
Investment Banking, on the other hand, connects companies to investors and big financial opportunities. It’s what helps businesses raise money from stock markets, sell bonds, or even buy other companies. For example, when Amazon bought Whole Foods for $13.7 billion, investment bankers were behind the deal, structuring the financing and negotiations.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| Aspect | Corporate Finance | Investment Banking |
| Main Role | Managing a company’s money and strategy | Helping companies raise money and make deals |
| Focus Area | Internal decision-making | External financial markets |
| Example | Deciding whether to launch a new product | Taking a company public with an IPO |
| Goal | Long-term growth and profit stability | Fast-paced capital raising and deal-making |
| Workplace | Within corporations | In banks or financial institutions |
Simply put, what is corporate finance about? It’s keeping the company’s financial engine running, while investment banking fuels it with more power. Together, they ensure business continuity and expansion.
In fact, the global investment banking market was valued at over $157 billion in 2024 and continues to grow as companies seek more strategic mergers, acquisitions, and IPOs. Meanwhile, corporate finance teams are becoming more data-driven, using analytics and AI to make smarter financial decisions and reduce risk.
In short, both are vital corporate finance focuses on how money is used, while investment banking focuses on how money is raised. Together, they shape the financial strength and future direction of businesses worldwide.
Modern Trends in Corporate Finance

Due to shifting business priorities, worldwide markets, and technology, corporate finance is moving more quickly than ever. Companies today aren’t just balancing budgets; they’re using data analytics, automation, and sustainability goals to shape smarter financial strategies. Let’s explore the top trends transforming corporate finance in 2025 and beyond.
1. Digital Transformation and Automation
Technology is revolutionizing how finance teams work. Over 70% of CFOs now use AI or RPA to automate repetitive tasks, highlighting how what corporate finance is today depends on data and automation. This shift frees up teams to focus more on strategic decision-making rather than manual data crunching.
2. Data-Driven Financial Decision-Making
Gone are the days when finance relied on gut instincts. Today, companies leverage real-time analytics to predict cash flow, assess risks, and plan investments. Platforms like SAP, Oracle, and Power BI allow CFOs to visualize company-wide performance instantly. In fact, data-driven companies are 23 times more likely to outperform competitors in profitability, according to McKinsey.
3. Sustainability and ESG Financing
Corporate finance is no longer just about profits; it’s about purpose too. The rise of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing has transformed how companies manage funds. In 2025, global ESG assets are expected to surpass USD $50 trillion, pushing companies to adopt green bonds, carbon accounting, and sustainable investment strategies that attract responsible investors.
4. Strategic Risk Management and Cybersecurity
With the rise of digital systems, cybersecurity has become a financial issue. Data breaches cost companies $4.45 million per incident (IBM, 2025). Hence, what is corporate finance today includes cyber-risk budgeting and resilience planning. Corporate finance teams now play a key role in allocating budgets for cyber resilience and ensuring risk-adjusted financial stability in a volatile world.
5. Globalization and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The finance world is becoming borderless. Businesses are using blockchain technology and decentralized finance platforms to manage cross-border transactions more efficiently. According to Deloitte, nearly 40% of Fortune 500 companies are exploring blockchain-based solutions to simplify international payments and reduce transaction costs.
6. The Evolving Role of the CFO
Modern CFOs are no longer just “number crunchers.” They are strategic leaders driving innovation, digital investments, and sustainable growth. With 82% of CFOs involved in strategy, what is corporate finance has transformed into a strategic growth engine fueling innovation and global expansion.
In essence, the future of Corporate Finance is smart, digital, and purpose-driven. The focus has shifted from simply managing money to creating value through data, technology, and sustainability. As these trends continue to accelerate, corporate finance will remain the engine behind every company’s long-term success.
Conclusion:
At its core, Corporate Finance is what keeps every business moving forward. It’s not just about managing money; it’s about making smart choices that help companies grow, adapt, and stay strong in a changing world. From deciding how to invest profits to planning major expansions or acquisitions, corporate finance guides the big financial decisions that shape a company’s future.
In today’s world, technology and data are transforming how these decisions are made. Tools powered by AI and analytics are helping businesses forecast trends, manage risks, and find smarter ways to use their capital. Meanwhile, the rise of sustainability and ESG investing shows that companies are thinking beyond profits; they’re focused on long-term impact and responsible growth.
Simply put, corporate finance is where strategy meets numbers. Whether it’s a small business planning its next move or a global giant funding innovation, good financial management is what keeps success sustainable. Understanding how corporate finance works isn’t just useful for finance professionals; it’s essential for anyone who wants to see how businesses grow and create value in the modern economy.
FAQs on Corporate Finance
1. What is Corporate Finance in simple terms?
Corporate Finance is the area of finance that deals with how a company manages its money, from raising capital to investing in projects and maximizing profits. In simple words, it’s about how businesses plan, fund, and grow financially while keeping risks low.
2. What are the three main areas of Corporate Finance?
The three key areas are:
Capital Budgeting: Deciding where to invest company funds (like new products or facilities).
Capital Structure: Determining the right mix of debt and equity to fund growth.
Working Capital Management: Managing short-term cash flow and day-to-day expenses.
3. How is Corporate Finance different from Investment Banking?
Corporate Finance focuses on internal financial decisions how a company uses its money.
Investment Banking, on the other hand, helps companies raise money from outside investors and manage big transactions like IPOs or mergers.
4. Why is Corporate Finance important for businesses?
Because every major business decision, whether to expand, acquire, or launch a new product, depends on financial planning. Effective corporate finance ensures a company stays profitable, stable, and ready for future growth.
5. What are some examples of Corporate Finance in real life?
○ Apple, issuing bonds to fund innovation.
○ Tesla, investing in new gigafactories.
○ Amazon, acquiring smaller firms to expand its logistics.
These are all real examples of companies making corporate finance decisions to strengthen their business.
6. What are the latest trends shaping Corporate Finance in 2025?
Some key trends include the rise of AI automation, ESG investing, blockchain adoption, and data-driven financial forecasting. These innovations are helping companies make smarter, faster, and more ethical financial choices.
7. What skills are needed to build a career in Corporate Finance?
Professionals need a mix of technical and strategic skills, such as:
Financial modeling and analysis
Strategic planning
Understanding capital markets
Risk management
Proficiency in digital tools like Excel, Power BI, or SAP
8. What’s the future of Corporate Finance?
The future is highly digital and data-driven. As AI, blockchain, and sustainability reshape finance, the role of corporate finance professionals will expand from managing money to driving innovation and long-term business value.


















