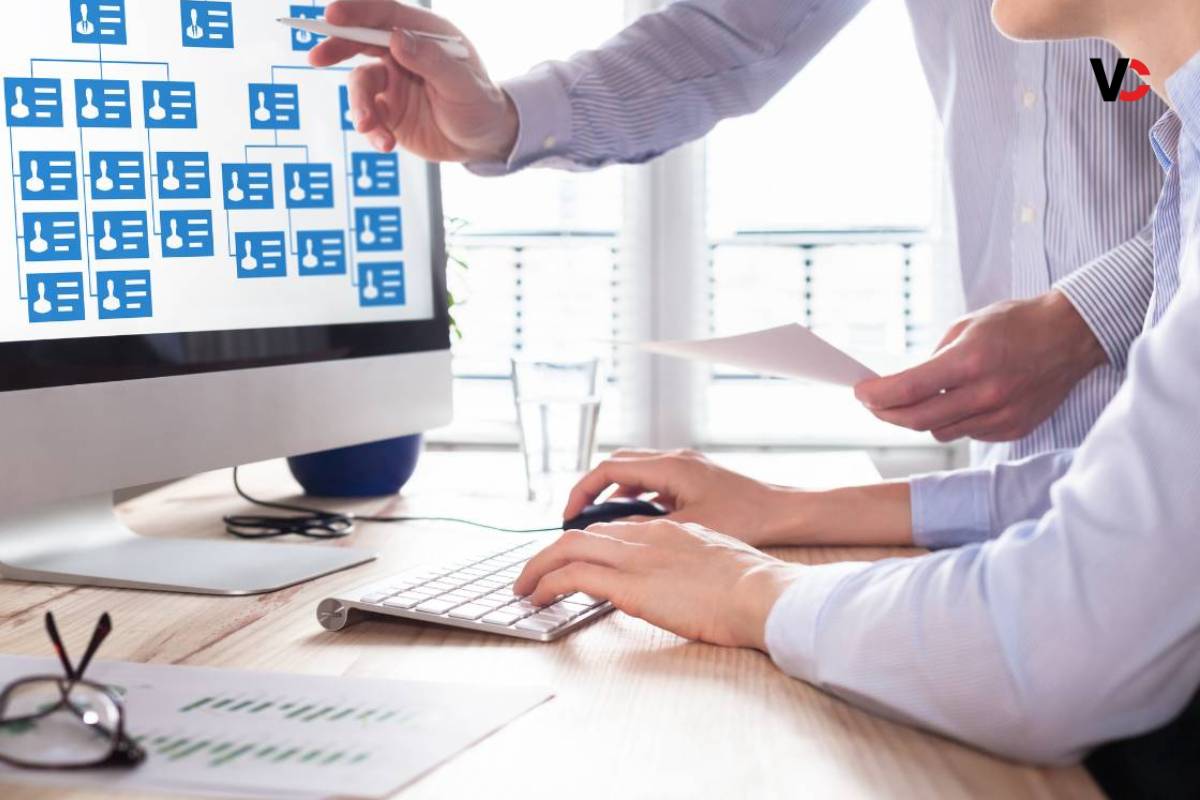
Organizational Structure is the blueprint that defines the hierarchical arrangement of roles, responsibilities, and communication channels within a company. It serves as the framework through which tasks are delegated, decisions are made, and resources are allocated. A well-designed Organizational Structure not only facilitates coordination and efficiency but also supports the achievement of strategic goals and objectives. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Organizational Structure, exploring its key elements, common types, and best practices for implementation.
Key Elements of Organizational Structure
The organizational structure serves as the backbone of any successful business, providing the framework through which roles, responsibilities, and communication channels are defined. At its core, the key elements of organizational structure dictate how power, authority, and decision-making flow within an organization. Understanding these fundamental elements is crucial for leaders and managers seeking to optimize efficiency, promote accountability, and foster collaboration among team members. By identifying and mastering these key elements, organizations can build a solid foundation that supports their strategic objectives, enhances operational effectiveness, and drives sustainable growth in today’s competitive landscape.
1. Hierarchy
At the heart of any Organizational Structure lies the hierarchical arrangement of authority and responsibility. This vertical distribution of power establishes reporting relationships and delineates the chain of command from top management to frontline employees.
2. Departments and Divisions
Organizational Structure typically consists of various departments or divisions, each responsible for specific functions or activities. These units may be organized by function, product, geography, or customer segment, depending on the company’s objectives and industry.
3. Roles and Responsibilities
Clear delineation of roles and responsibilities is essential for effective decision-making and accountability within an organization. Each position within the structure should have well-defined duties, authority, and reporting relationships.
4. Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital for the smooth functioning of an organization. Organizational Structure determines the flow of information within the company, including formal channels such as hierarchical reporting lines and informal networks.
5. Span of Control
The span of control refers to the number of subordinates directly supervised by a manager. A narrow span of control implies fewer direct reports, allowing for closer supervision and more hierarchical levels, while a wider span of control fosters decentralization and autonomy.
Common Types of Organizational Structure
Organizational structure plays a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics and operations of a company. Among the key considerations in designing an effective structure is determining the appropriate type to suit the organization’s objectives, culture, and industry. Common types of structures offer distinct approaches to organizing departments, roles, and decision-making processes. Each type has its advantages and challenges, impacting factors such as communication, efficiency, and collaboration within the organization. Understanding these common types of structure is essential for leaders seeking to optimize their company’s structure for success and adaptability in a competitive business environment.
1. Functional Structure
In a functional Organizational Structure, departments are organized based on specialized functions such as marketing, finance, operations, and human resources. This type of structure promotes efficiency and expertise within functional areas but may lead to silos and limited cross-functional collaboration.
2. Divisional Structure
A divisional Organizational Structure groups employees based on products, services, or geographic regions. Each division operates as a separate entity with its own resources and decision-making authority, allowing for flexibility and focus but potentially duplicating functions and increasing coordination challenges.
3. Matrix Structure
A matrix Organizational Structure combines elements of both functional and divisional structures, creating dual reporting relationships. Employees report to both functional managers and project managers, enabling specialization and project-focused collaboration but requiring strong communication and conflict-resolution skills.
4. Flat Structure
In a flat Organizational Structure, there are few hierarchical levels, with minimal layers of management between frontline employees and top executives. This promotes agility, quick decision-making, and a collaborative culture but may lead to ambiguity in roles and responsibilities.
5. Hierarchical Structure
A hierarchical Organizational Structure features a clear chain of command, with decision-making authority concentrated at the top and cascading down through various levels of management. While this structure provides stability and accountability, it can stifle innovation and hinder agility.
Best Practices for Implementing Organizational Structure

Implementing organizational structure changes can be a daunting task for any organization. However, with careful planning and adherence to best practices, these changes can lead to improved efficiency, communication, and alignment with strategic goals. Best practices for implementing structure changes encompass various aspects, including alignment with strategy, clear communication, employee involvement, flexibility, and ongoing evaluation. By following these best practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of organizational change effectively, fostering a culture of adaptability and continuous improvement for long-term success.
1. Align with Strategy
Organizational Structure should align with the company’s strategic goals and objectives, supporting its mission, vision, and values. Consider factors such as industry dynamics, competitive landscape, and growth aspirations when designing the structure.
2. Flexibility and Adaptability
A successful Organizational Structure should be flexible enough to accommodate changes in the external environment, such as shifts in market conditions, technological advancements, or regulatory requirements. Regular review and adaptation of the structure are essential to ensure continued relevance and effectiveness.
3. Clear Communication
Transparent communication is critical during the implementation of Organizational Structure changes. Clearly communicate the rationale behind the changes, expectations for employees, and any support or resources available to facilitate the transition.
4. Employee Involvement
Involve employees in the design and implementation of Organizational Structure changes to gain buy-in and foster ownership. Solicit feedback, address concerns, and provide opportunities for training and development to support employees through the transition.
5. Monitor and Evaluate
Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the Organizational Structure in achieving its intended objectives. Collect feedback from employees, track key performance indicators, and adjust the structure as needed to address emerging challenges or opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Organizational Structure is a fundamental aspect of any company’s operations, shaping its culture, efficiency, and ability to achieve strategic objectives. By understanding the key elements, common types, and best practices for implementation, organizations can design and deploy structures that support agility, collaboration, and innovation. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the ability to adapt and optimize Organizational Structure will be critical for staying competitive and driving sustainable growth in the dynamic marketplace.
Also Read: Unlocking Success Through Effective Stakeholder Engagement Strategies



















