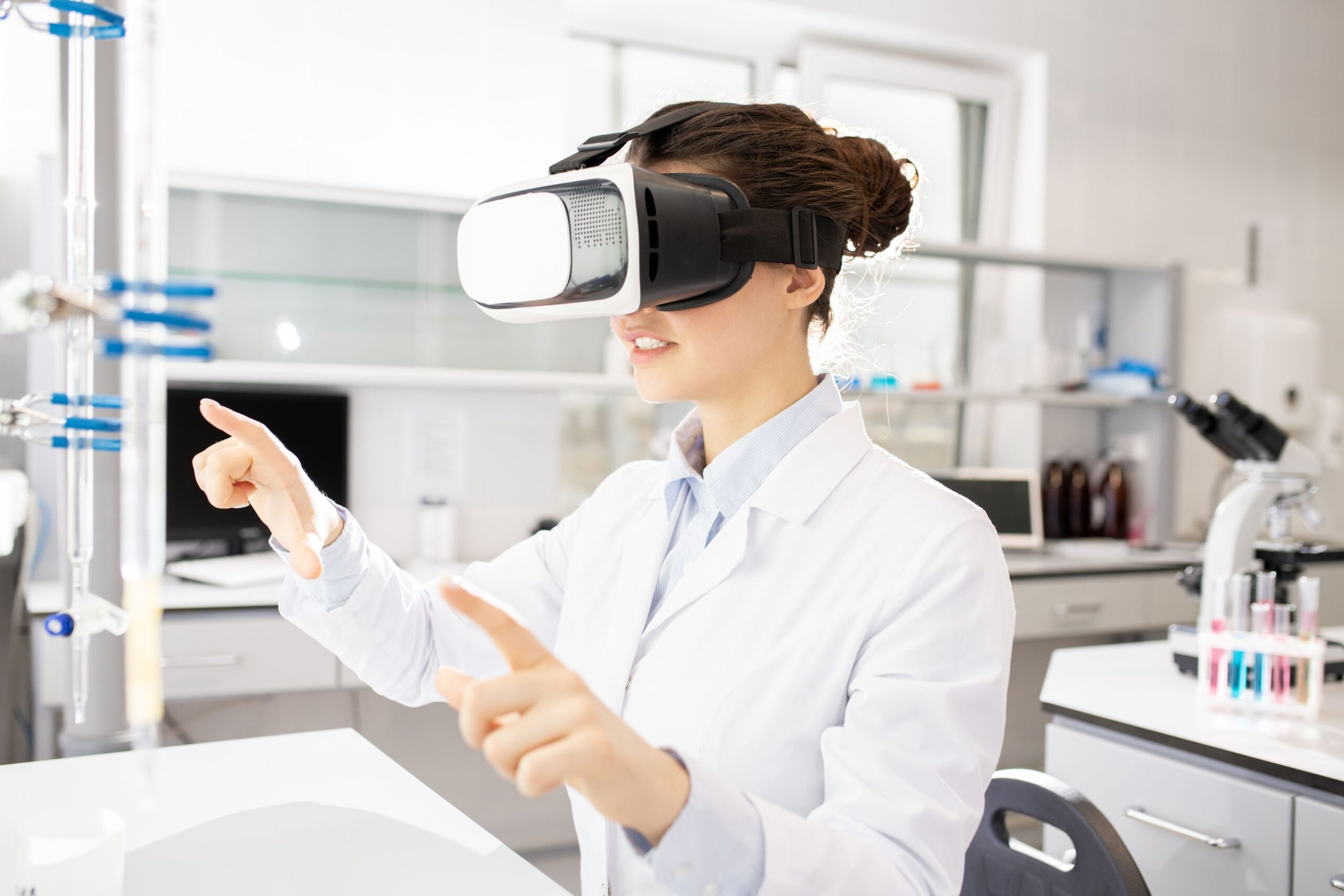
Hospitals aren’t exactly known for comfort. Patients often feel a surge of anxiety, wearing them down mentally before any medical procedure, or maybe slowing down their recovery. However, incorporating virtual reality in healthcare has changed the whole aspect of patient care.
The advancement of technology has led to improved medical outcomes in healthcare, with many hospitals and clinics using it for various treatments. For example, therapy clinics have started using virtual reality to treat PTSD by creating a safer environment through a headset and making rehab a little less miserable. Pediatric units are using VR to distract children during procedures. Treatment for stroke patients has become more effective due to the use of gamified rehabilitation environments.
Virtual reality isn’t just confined to gaming purposes. The healthcare sector has been successful in helping patients prepare for surgeries and even confront mental traumas in a safe, controlled environment. In this article, we’ll discuss how virtual reality in healthcare is changing, its applications across various domains, and the future of patient care.
What is Virtual Reality in Healthcare?
Virtual reality in healthcare uses interactive, computer-generated environments to simulate real medical scenarios. These environments are accessed through headsets, like Meta Quest, HTC Vive, or specialized medical-grade devices that fully immerse the user in a virtual 3D environment. In these spaces, medical professionals can train, patients can undergo therapy, and clinicians can guide procedures.
VR is built with anatomical precision, customized treatment plans, physiological data integration, and response-based interaction. Some integrate haptics (tactile feedback), while others include voice cues or biometric sensors. Machine learning and AI also make virtual reality (VR) experiences more immersive and responsive. This results in higher engagement, deeper understanding, and, often, faster recovery.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Healthcare
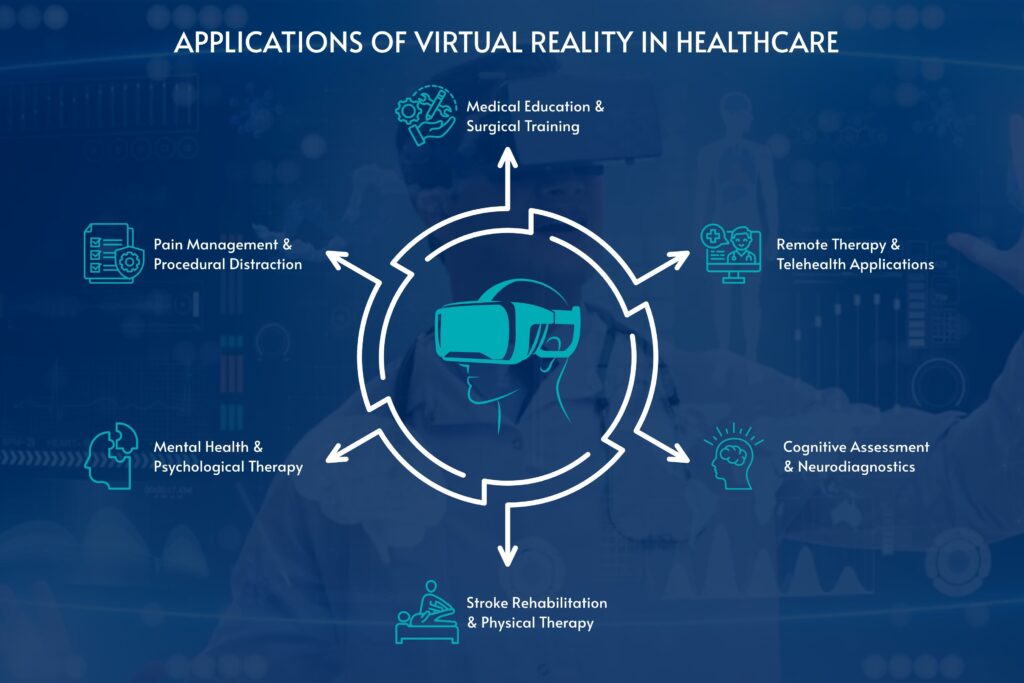
1. Medical Education & Surgical Training
Medical schools and hospitals have long struggled to train students and residents without putting patients at risk. VR solves that with immersive training tools. Students no longer need to wait for cadavers or observe passively in operating rooms; they can enter a high-fidelity digital human body and explore organs, vessels, or systems layer by layer.
Surgeons use VR platforms to practice procedures before operating. These procedures are patient-specific and built from actual MRI and CT scans. A neurosurgeon can walk through a tumor resection procedure multiple times, rehearsing tricky angles and potential complications. VR training reduces surgical error rates, increases confidence, and improves patient outcomes.
2. Pain Management & Procedural Distraction
Pain is emotional and cognitive. Traditional medication is efficient but prone to having specific side effects. Virtual reality in healthcare offers a more non-invasive, drug-free approach. VR provides a visual escape for burn patients undergoing dressing changes (often described as some of the most painful procedures in medicine). For example, a VR headset exposes patients to forests, ocean reefs, or calming surroundings. This helps by significantly shifting their focus and reducing the brain’s pain response.
In chemotherapy wards, children wear VR headsets during infusions, reducing fear and discomfort. In dental clinics, anxious patients use VR to relax during extractions. Even labor wards are experimenting with VR to help women focus during contractions. The analgesic effect of VR isn’t just anecdotal; it’s been validated in several clinical studies that show a measurable reduction in pain scores and anxiety markers.
3. Mental Health & Psychological Therapy
Exposure therapy is a standard treatment for PTSD, phobias, and severe anxiety, but live exposure can be risky or impractical. VR gives therapists control and patients’ safety. Veterans dealing with war trauma can revisit situations in virtual, controlled environments and process their responses gradually. Individuals who fear flying can “board” a virtual plane and learn to manage their reactions.
Guided meditation apps inside VR environments help manage depression and stress. Cognitive behavioral therapy modules in VR provide interactive challenges, mood tracking, and real-time coping strategies. The immersive nature helps with engagement and retention, especially in younger patients or those who struggle with conventional talk therapy.
4. Stroke Rehabilitation & Physical Therapy
Recovering from a stroke requires repetition, consistency, and motivation, which is challenging to maintain over months. VR rehab systems change that by turning monotonous exercises into interactive tasks. A patient might reach for virtual apples to improve upper limb function or follow a trail in a forest path to work on gait and balance.
These systems are fun and bright. They track motion, provide live feedback, and adapt difficulty based on progress. Therapists can monitor remotely and fine-tune exercises. Patients feel in control and engaged, which dramatically improves compliance.
For those in remote or underserved areas, virtual reality in healthcare offers access to quality rehab from home. The emotional boost from seeing visible progress inside a virtual environment often motivates patients to keep going.
5. Cognitive Assessment & Neurodiagnostics
Detecting cognitive decline, like early-stage Alzheimer’s, often requires comprehensive, repetitive tests. VR introduces a new way to assess memory, spatial reasoning, executive function, and reaction time. One example includes simulating a kitchen task: a patient must find ingredients, remember a recipe, and complete steps, all inside a virtual kitchen.
This level of interaction offers better insight into cognitive function than pen-and-paper tests. VR-based assessments capture eye movement, reaction time, motor response, and error patterns, offering clinicians a more complete neurological understanding.
In disorders like Parkinson’s or ADHD, VR tools help monitor attention spans, tremor patterns, and even emotional responses. It’s a non-invasive way to track brain health over time.
6. Remote Therapy & Telehealth Applications
Access to therapy and rehab is a significant barrier for rural populations, older people, and those with mobility issues. VR is solving that by bringing care into the home. All that’s needed is a headset and an internet connection. Patients can undergo physical therapy, mental health support, or pain management sessions while clinicians supervise in person.
Apart from cost savings, this improves healthcare access. A cancer survivor in a remote village can now meet a top rehabilitation expert virtually. Veterans can attend weekly therapy without commuting. With voice input, motion tracking, and remote data logging, VR makes telehealth deeply interactive, not just a Zoom call.
Benefits of Virtual Reality in Healthcare
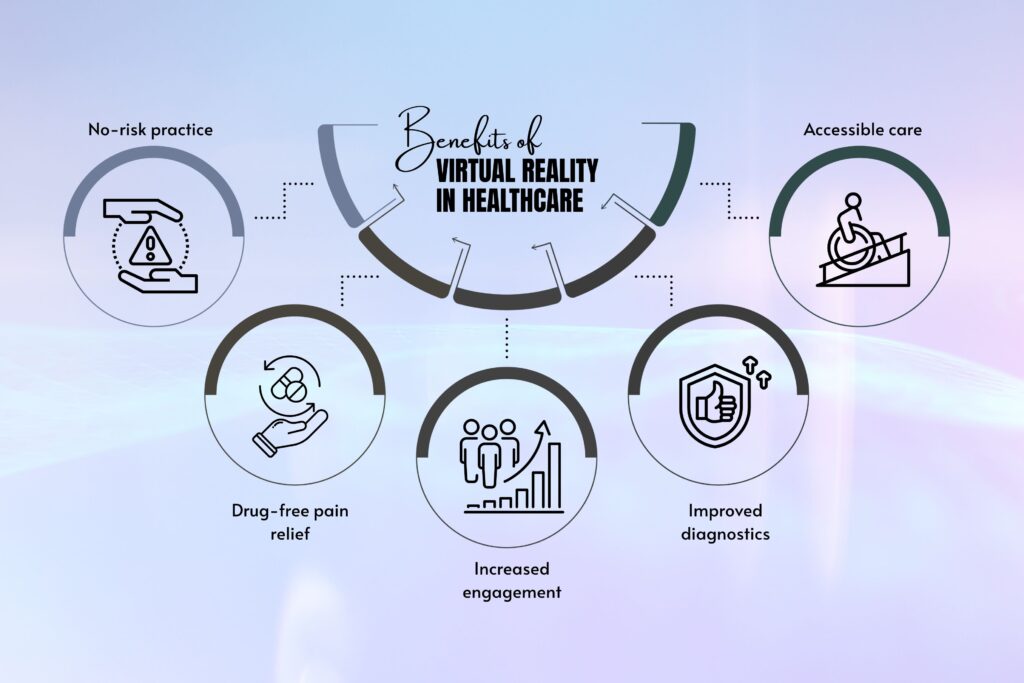
- No-risk practice: VR training lets clinicians make mistakes without harming real patients.
- Drug-free pain relief: Useful for chronic pain, burns, chemo, and labor without side effects.
- Increased engagement: Rehab patients stick with programs longer when they feel immersed.
- Improved diagnostics: Neuro assessments are richer and more behaviorally accurate.
- Accessible care: Therapy can be delivered to patients who would otherwise be left out.
The Future of VR and AI in Healthcare
VR’s next leap is happening through artificial intelligence. AI allows VR systems to adapt in real-time. A rehab module can now analyze your movement and adjust difficulty mid-session. A surgical simulation can give corrective feedback based on hand motion tracking. Mental health apps can detect voice stress and recommend calming exercises or alert therapists if needed.
AI-integrated VR also enables predictive insights. Systems can predict early warning signs of decline or non-compliance by observing trends across thousands of patient sessions. In training, it evaluates surgeon performance across metrics like precision, speed, and accuracy, turning subjective skill into measurable outcomes. As AI models grow smarter, expect virtual environments to become personalized, proactive, and even anticipatory.

Top Healthcare Technology Trends Driving Change in the Sector
Here are the Top 7 Healthcare Technology Trends: 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning 2. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring 3. Blockchain Technology for Health Data Security
Software & Platforms Powering the VR Shift
A few major companies are building healthcare-focused VR tools. These tools are being integrated into hospital workflows. They’re HIPAA-compliant, evidence-based, and expanding access to immersive care globally.
- Osso VR: Widely used in surgical training; validated for skill improvement.
- AppliedVR: FDA-cleared for chronic pain relief with strong clinical backing.
- XR.Health: Offers VR-based telehealth with remote therapist access.
- FundamentalVR: Combines haptics with VR for realistic surgical simulation.
- Neuro Rehab VR: Focused on stroke and neurological condition recovery.

Conclusion
Virtual reality in healthcare is changing how we teach medicine, how we treat pain, how we diagnose decline, and how we deliver therapy.
What started as a headset experiment is now an essential tool across multiple care domains. With AI, remote access, and data integration, VR proves that modern healthcare doesn’t just need better doctors and tools. It doesn’t replace human care. It enhances it by making healing more immersive, more engaging, and more accessible than ever.


















