In the competitive landscape of modern business, standing out from the crowd is crucial for sustained success and growth. The Blue Ocean Strategy offers a revolutionary approach to strategic planning, enabling organizations to break free from the constraints of traditional competition and carve out uncontested market space. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the principles, strategies, and real-world examples of the Blue Ocean Strategy, exploring how businesses can chart their course to success in uncharted waters.
Understanding the Blue Ocean Strategy:
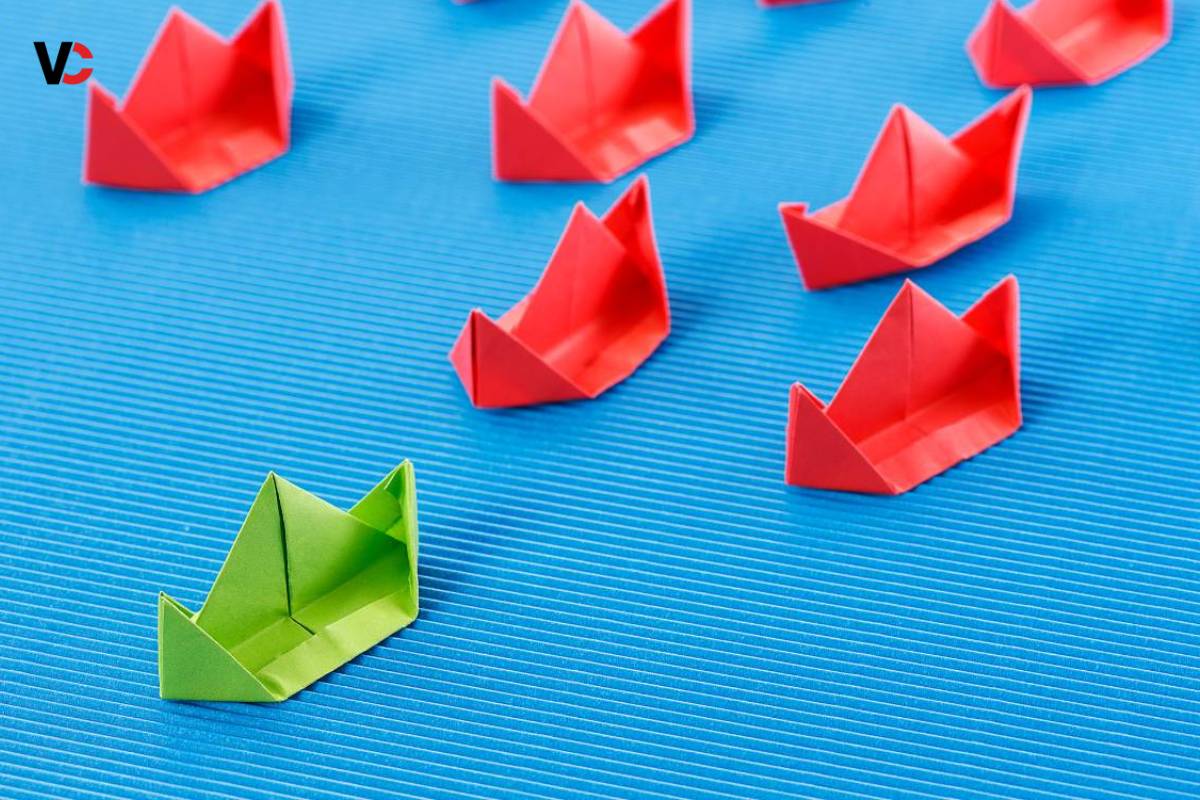
The Blue Ocean Strategy, conceived by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne, represents a departure from conventional business paradigms. It urges organizations to break away from the competitive battlegrounds of existing markets, often termed as “red oceans,” characterized by cutthroat competition and diminishing profit margins. Instead, the strategy encourages the pursuit of untapped market spaces, referred to as “blue oceans,” where competition is irrelevant and opportunities abound.
Key Components of the Blue Ocean Strategy:

1. Innovation
Central to the Blue Ocean Strategy is innovation – not merely incremental improvements, but transformative breakthroughs that redefine industry boundaries and create new demand.
2. Value Creation
Organizations must focus on creating exceptional value for customers, addressing their unmet needs, and delivering solutions that resonate deeply with their preferences and aspirations.
3. Differentiation
By offering products or services that stand out from the crowd, organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors and establish a unique position in the marketplace.
4. Strategic Positioning
Successful implementation of the Blue Ocean Strategy requires careful strategic positioning, ensuring alignment between the organization’s strengths, market opportunities, and customer preferences.
5. Execution Excellence
Execution is paramount in realizing the potential of the Blue Ocean Strategy. It involves translating strategic insights into actionable plans, mobilizing resources effectively, and driving organizational alignment and commitment.
In essence, the Blue Ocean Strategy represents a shift in mindset – from competing in overcrowded markets to creating new market spaces where competition is irrelevant and value innovation reigns supreme. It empowers organizations to chart their own course, discover untapped opportunities, and chart a path to sustainable growth and profitability.
Key Principles of the Blue Ocean Strategy:

1. Value Innovation
The Blue Ocean Strategy emphasizes the importance of value innovation, which involves simultaneously pursuing differentiation and low cost. By creating products or services that offer unique value to customers at a lower cost, organizations can break away from the trade-off between value and price commonly seen in red ocean markets.
2. Focus on Non-customers
Traditional market strategies often revolve around targeting existing customers within a specific industry or demographic. In contrast, the Blue Ocean Strategy encourages organizations to expand their market reach by focusing on non-customers – those who are currently underserved or excluded by existing market offerings.
3. Eliminate, Reduce, Raise, Create (ERRC) Grid
The ERRC grid is a key tool in the Blue Ocean Strategy framework, helping organizations identify strategic options for value innovation. By evaluating factors that can be eliminated, reduced, raised, or created across different industry attributes, organizations can uncover opportunities to redefine market boundaries and create blue oceans.
4. Pursue Differentiation and Relevance
Blue ocean markets are characterized by innovation and relevance, offering products or services that address unmet needs or provide unique value propositions. Organizations must focus on differentiation and relevance to stand out in the marketplace and attract customers away from existing alternatives.
Real-World Examples of the Blue Ocean Strategy:

1. Cirque du Soleil
Cirque du Soleil revolutionized the entertainment industry by combining elements of traditional circus acts with high-quality theatrical performances. By targeting adults rather than children and families, Cirque du Soleil created a new market space that transcended the limitations of traditional circuses.
2. Yellow Tail Wine
Yellow Tail Wine disrupted the wine industry by offering approachable, fruit-forward wines at an affordable price point. By simplifying wine selection and packaging, Yellow Tail appealed to a broader audience of casual wine drinkers, expanding the market and challenging established competitors.
3. Nintendo Wii
Nintendo Wii redefined the gaming industry with its innovative motion-controlled gaming console. By targeting non-gamers, such as families and seniors, Nintendo Wii expanded the gaming market and introduced a new way to play video games, positioning itself in a blue ocean of uncontested market space.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Blue Ocean Strategy offers a compelling framework for business success, implementing it effectively requires careful planning, execution, and adaptation. Organizations may face challenges such as resistance to change, uncertainty about market acceptance, and the need for continuous innovation. However, by embracing the principles of value innovation, customer-centricity, and strategic agility, organizations can overcome these challenges and unlock new opportunities for growth and differentiation.
Implementing the Blue Ocean Strategy presents both challenges and opportunities for organizations seeking to redefine their competitive landscape and carve out new market spaces.
Challenges:
- Resistance to ChangeOne of the primary challenges organizations encounter is internal resistance to change. Employees and stakeholders accustomed to traditional business models may be reluctant to embrace innovative strategies and may fear the unknown.
- Market Uncertainty: Venturing into uncharted waters entails inherent risks and uncertainties. Organizations may face challenges in accurately gauging market demand, understanding customer preferences, and predicting competitor reactions.
- Continuous Innovation: Sustaining competitive advantage in blue oceans requires a relentless commitment to innovation. Organizations must continually adapt and evolve their offerings to meet evolving customer needs and market dynamics.
- Resource Allocation: Pursuing blue ocean opportunities often requires significant investments in research, development, and marketing. Allocating resources effectively while balancing short-term demands and long-term objectives can be a daunting task.
Opportunities:
- Market Leadership: Successfully implementing the Blue Ocean Strategy can position organizations as market leaders in untapped market spaces, offering opportunities for growth and dominance.
- Differentiation: By focusing on value innovation and differentiation, organizations can create unique value propositions that set them apart from competitors and attract new customers.
- Increased Profitability: Blue oceans typically offer higher profit margins compared to crowded red ocean markets, providing opportunities for increased profitability and revenue growth.
- Customer Engagement: Creating innovative products or services tailored to unmet customer needs can foster deeper engagement and loyalty among customers, driving long-term relationships and brand advocacy.
- Strategic Flexibility: Embracing the Blue Ocean Strategy fosters strategic agility and adaptability, enabling organizations to respond effectively to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities.
While challenges may arise in the pursuit of blue ocean opportunities, organizations that embrace the principles of value innovation, customer-centricity, and strategic agility can overcome obstacles and unlock new avenues for growth, differentiation, and success. By navigating these challenges thoughtfully and seizing opportunities strategically, organizations can chart a course to sustained prosperity in uncharted waters.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Blue Ocean Strategy provides a transformative approach to strategic thinking, enabling organizations to break free from the constraints of traditional competition and create uncontested market space. By focusing on value innovation, targeting non-customers, and pursuing differentiation and relevance, organizations can chart their course to success in blue oceans of opportunity. As businesses navigate the ever-changing landscape of the global marketplace, the Blue Ocean Strategy offers a compass for navigating uncharted waters and unlocking new avenues for growth, profitability, and sustainable success.
Also Read: Exploring the Pros and Cons of Veneers: A Comprehensive Guide