In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, effective management of product lifecycles is crucial for companies striving to maintain a competitive edge. Product lifecycle management (PLM) is a strategic approach that encompasses the entire lifespan of a product, from its inception through its development, launch, and eventual retirement. This article delves into the concept of product lifecycle management, its significance, the phases involved, and how organizations can leverage PLM to drive efficiency and innovation.
What is Product Lifecycle Management?
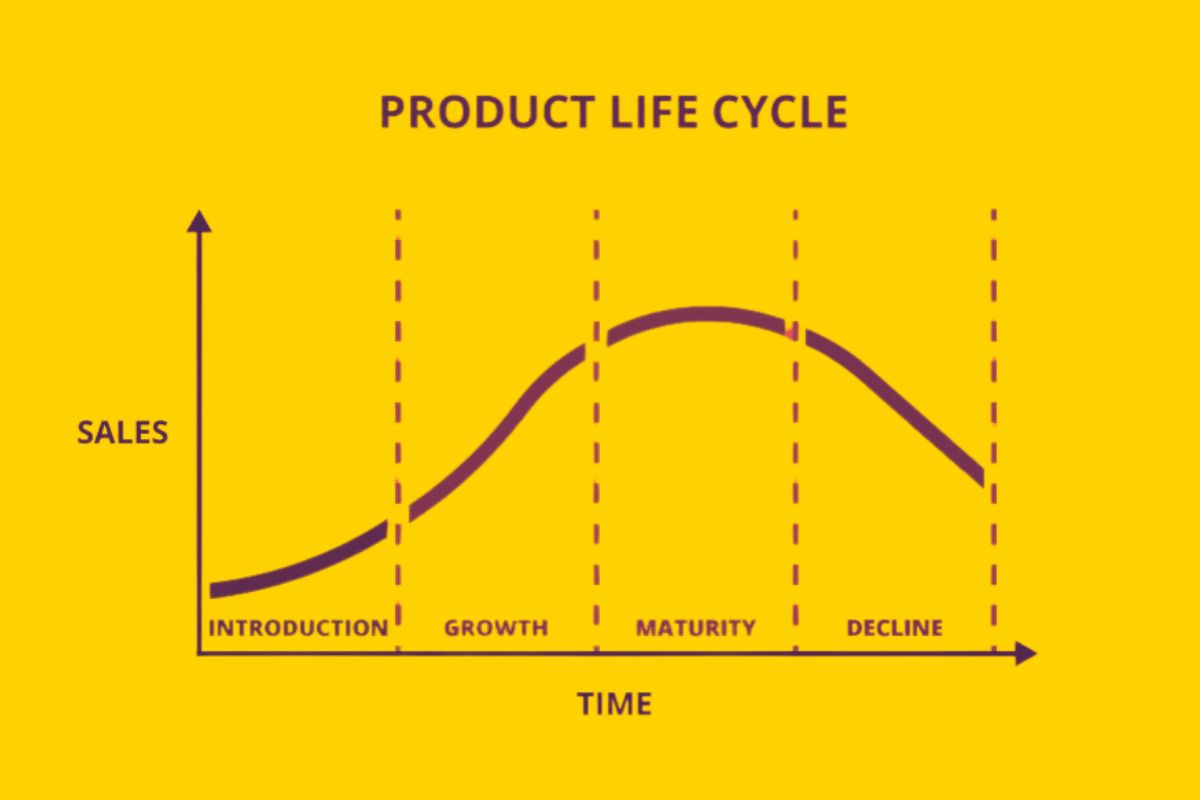
Product lifecycle management refers to the systematic management of a product’s lifecycle from its initial concept and design to its discontinuation. PLM integrates people, processes, business systems, and information to facilitate the efficient management of a product throughout its life. By adopting a robust PLM strategy, businesses can improve product quality, reduce time to market, and enhance collaboration across departments.
Importance of Product Lifecycle Management
Implementing an effective product lifecycle management strategy offers numerous benefits for organizations:
- Enhanced Collaboration: PLM fosters collaboration among different teams, including engineering, marketing, manufacturing, and sales. By ensuring that all stakeholders have access to real-time data and insights, businesses can make informed decisions and respond to market changes promptly.
- Improved Efficiency: PLM streamlines processes and reduces redundancies. By automating various tasks, such as data entry and reporting, organizations can minimize errors and save valuable time, allowing teams to focus on innovation and strategic initiatives.
- Cost Reduction: By managing the product lifecycle effectively, businesses can identify potential issues early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of costly redesigns and recalls. This proactive approach not only saves money but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring a high-quality product.
- Faster Time to Market: In today’s fast-paced business environment, speed is critical. Effective PLM enables companies to expedite product development and launch processes, ensuring they can quickly respond to consumer demands and emerging trends.
- Sustainable Practices: With growing concerns about environmental impact, PLM helps organizations adopt sustainable practices by considering the product’s ecological footprint throughout its lifecycle. This includes materials sourcing, production methods, and end-of-life disposal, aligning with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
Phases of Product Lifecycle Management
The product lifecycle management process can be broken down into several key phases:

1. Concept and Development
The first phase involves ideation and conceptualization. This is where product ideas are generated based on market research, consumer feedback, and technological advancements. Teams collaborate to define the product’s requirements, features, and potential market fit. Prototyping and initial testing are crucial in this stage to assess feasibility.
2. Design and Engineering
Once a concept is validated, the design and engineering phase begins. This involves creating detailed specifications, drawings, and prototypes. Collaborative tools enable designers and engineers to work together seamlessly, ensuring that the product design aligns with market needs and technical requirements.
3. Manufacturing and Production
In this phase, the product moves into full-scale production. PLM systems play a vital role in managing production schedules, supply chain logistics, and quality control processes. Efficient manufacturing practices ensure that products are delivered on time and meet quality standards, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
4. Distribution and Marketing
Once produced, the product is ready for distribution. Marketing strategies are developed to promote the product to target audiences. PLM aids in tracking sales data, customer feedback, and market trends, allowing organizations to adjust their marketing efforts and distribution strategies accordingly.
5. Service and Support
After the product is launched, ongoing support and service are essential. This phase involves monitoring product performance, addressing customer inquiries, and managing warranties and service agreements. Feedback collected during this stage can inform future product iterations and enhancements.
6. Retirement and Disposal
Eventually, every product reaches the end of its lifecycle. The retirement phase involves phasing out the product, managing inventory, and ensuring proper disposal or recycling. Effective PLM helps organizations plan for product discontinuation while maximizing residual value.
Implementing Product Lifecycle Management
To successfully implement product lifecycle management, organizations should consider the following steps:

- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of the PLM strategy, including desired outcomes, key performance indicators (KPIs), and timelines.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select PLM software and tools that align with your business needs. Look for solutions that integrate well with existing systems and provide robust data analytics capabilities.
- Foster a Collaborative Culture: Encourage cross-functional collaboration by breaking down silos and promoting open communication among teams. A culture of collaboration enhances the effectiveness of PLM initiatives.
- Provide Training and Support: Ensure that employees are adequately trained on PLM tools and processes. Ongoing support and resources can help teams adapt to new technologies and methodologies.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and assess the PLM strategy to identify areas for improvement. Collect feedback from stakeholders and incorporate lessons learned into future initiatives.
Conclusion
In an era where innovation and efficiency are paramount, product lifecycle management is a vital component of successful product development and management. By understanding the importance of PLM and its various phases, organizations can streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and ultimately deliver high-quality products that meet consumer needs. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace, effective PLM will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in driving growth and maintaining a competitive advantage.
Found this article valuable? Explore more insights in our Visionary CIOs.


















