Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder that occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormone to meet the body’s needs. This condition affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to a variety of symptoms that impact overall health and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various hypothyroidism symptoms, its causes, and how it can be managed effectively.
Understanding Hypothyroidism Symptoms:
1. Fatigue
One of the hallmark hypothyroidism symptoms is persistent fatigue. Individuals with an underactive thyroid may feel constantly tired, even after getting adequate rest. This fatigue can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
2. Weight Gain
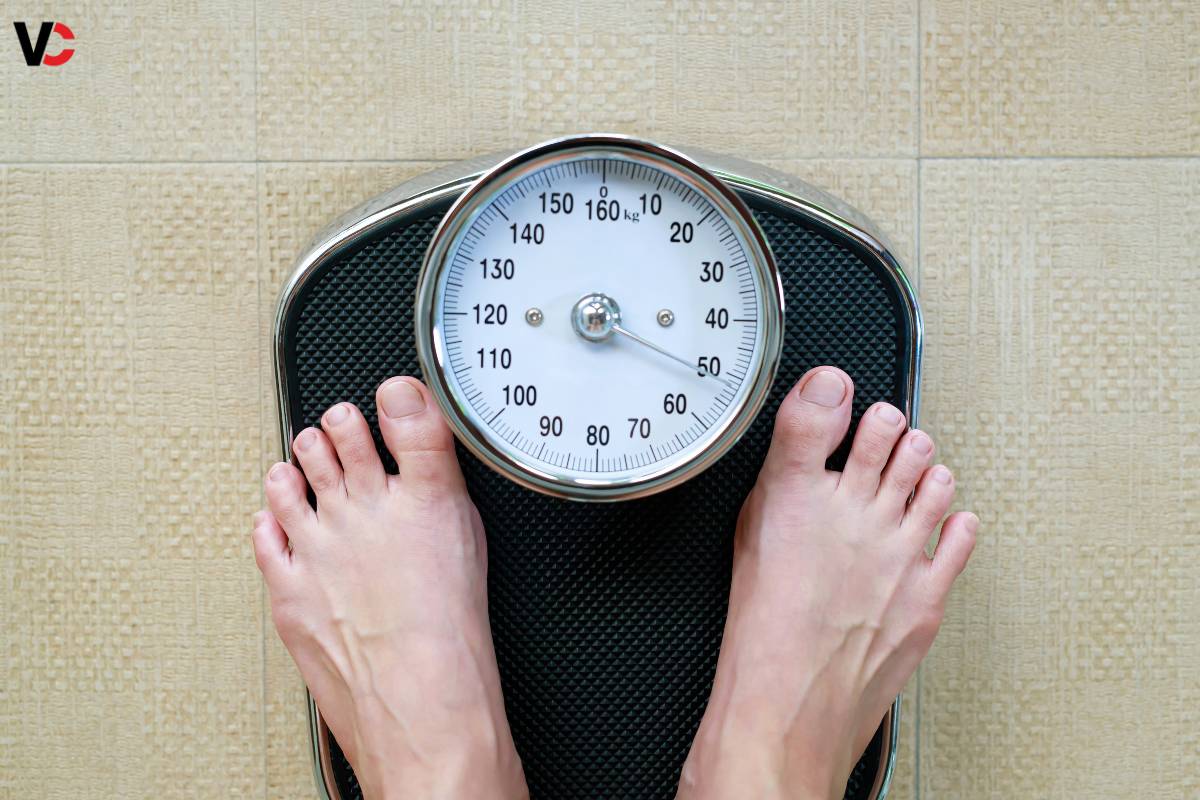

Weight gain is another common symptom of hypothyroidism. The slowed metabolism associated with an underactive thyroid can lead to unexplained weight gain, despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
3. Cold Sensitivity
People with hypothyroidism often experience intolerance to cold temperatures. They may feel excessively cold, even in environments that others find comfortable. This cold sensitivity can be particularly noticeable in the hands and feet.
4. Constipation
Hypothyroidism can affect the digestive system, leading to constipation. Slow bowel movements and difficulty passing stool are common symptoms experienced by individuals with an underactive thyroid.
5. Dry Skin and Hair
Dry, flaky skin and brittle hair are frequently reported symptoms of hypothyroidism. The lack of thyroid hormone can affect the skin’s ability to retain moisture, leading to dryness and irritation. Similarly, hair may become thin, dry, and prone to breakage.
6. Muscle Weakness
Weakness and achiness in the muscles are often reported by individuals with hypothyroidism. This can manifest as generalized muscle weakness or specific muscle pains, particularly in the arms and legs.
7. Joint Pain
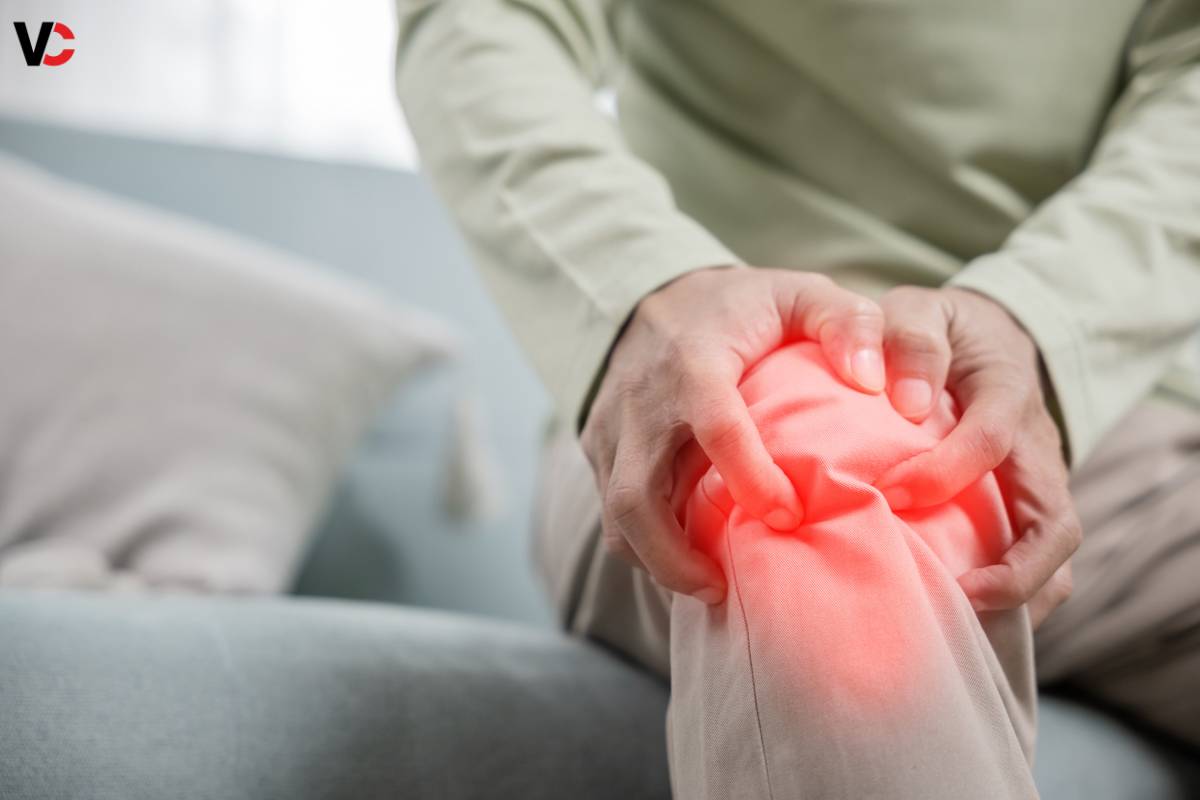

Joint pain and stiffness are common symptoms of hypothyroidism. The inflammation and swelling associated with an underactive thyroid can lead to discomfort, especially in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
8. Depression
Hypothyroidism can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to symptoms of depression. Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities once enjoyed are common among individuals with an underactive thyroid.
9. Memory Problems
Cognitive symptoms, such as memory problems and difficulty concentrating, can occur in people with hypothyroidism. These issues may affect daily functioning and productivity.
10. Irregular Menstrual Periods
Women with hypothyroidism symptoms may experience irregular menstrual periods or heavier-than-normal bleeding. Hormonal imbalances caused by an underactive thyroid can disrupt the menstrual cycle.
11. Decreased Libido
Hypothyroidism symptoms can also affect sexual function, leading to a decreased libido or loss of interest in sex. Hormonal changes associated with an underactive thyroid can contribute to sexual dysfunction.
12. Hoarseness
Hoarseness or changes in the voice can occur in individuals with hypothyroidism. This is often due to swelling and inflammation of the vocal cords caused by the condition.
13. Puffy Face
Some people with hypothyroidism may notice swelling and puffiness in the face, particularly around the eyes and cheeks. This can give the face a rounded appearance.
14. Slow Heart Rate
Hypothyroidism can affect heart function, leading to a slow heart rate or bradycardia. This can result in feelings of fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
15. Elevated Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels are commonly seen in individuals with hypothyroidism. The metabolic changes associated with an underactive thyroid can lead to an increase in LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol.
Causes of Hypothyroidism:
Hypothyroidism can have various causes, including:
1. Autoimmune Thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s Disease)
An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and decreased hormone production.
2. Thyroid Surgery
Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland can result in hypothyroidism.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation treatment for certain cancers, particularly in the head and neck area, can damage the thyroid gland and impair its function.
4. Medications
Certain medications, such as lithium and amiodarone, can interfere with thyroid hormone production.
5. Iodine Deficiency
Inadequate intake of iodine, a key nutrient for thyroid function, can lead to hypothyroidism in some cases.
6. Pituitary Disorders
Conditions affecting the pituitary gland, such as pituitary tumors or pituitary dysfunction, can disrupt the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which regulates thyroid hormone production.
Management of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism symptoms are typically managed with thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone medications to supplement the body’s natural production. The goal of treatment is to restore thyroid hormone levels to normal and alleviate symptoms.
Levothyroxine is the most commonly prescribed medication for hypothyroidism. It is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and is taken orally once daily. Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on individual response and thyroid function tests.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can also help manage hypothyroidism and improve overall well-being. These may include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Avoiding excessive iodine intake, particularly from supplements and certain foods.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to support metabolism and energy levels.
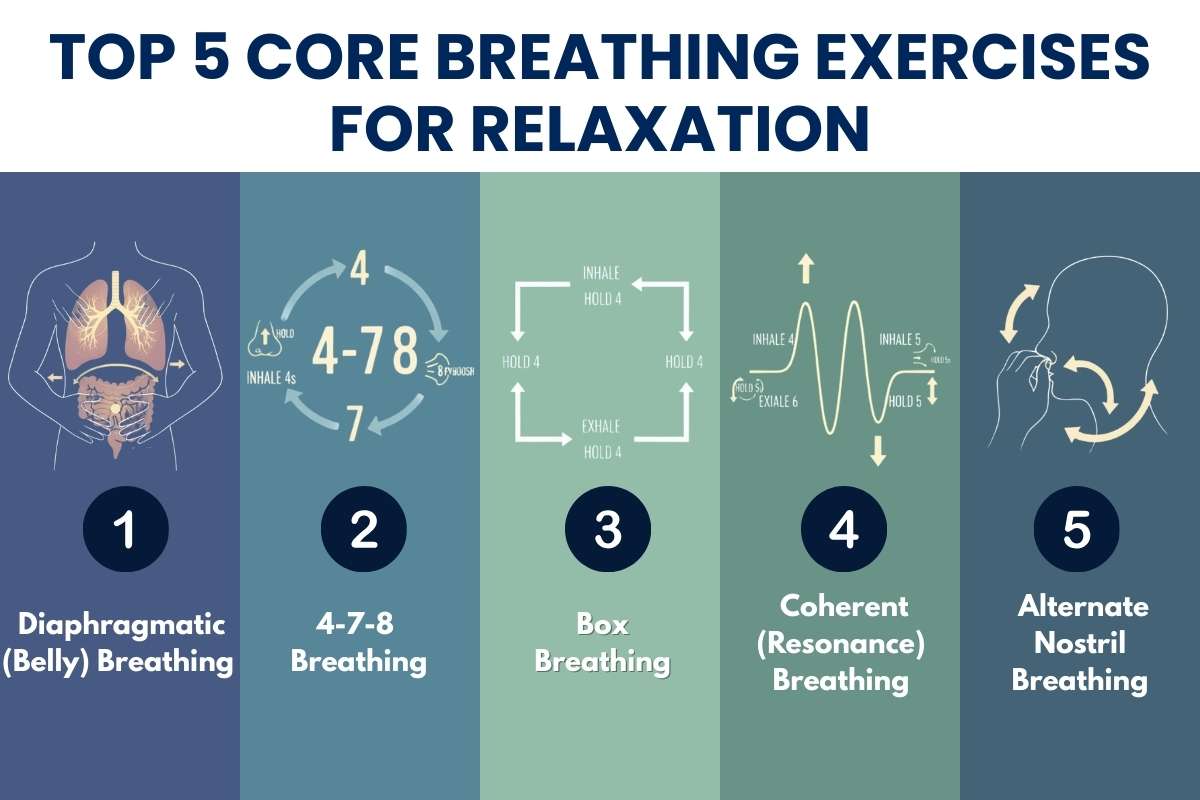
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Getting adequate sleep to support hormone balance and overall health.
Regular monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests is essential to ensure that thyroid hormone levels are within the optimal range. Adjustments to medication dosage may be needed over time, especially as factors such as age, weight, and other medical conditions can influence thyroid function.
Conclusion:
Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder characterized by a deficiency of thyroid hormone. The hypothyroidism symptoms can vary widely and may affect multiple systems in the body, including energy levels, metabolism, mood, and overall well-being. By understanding the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism, individuals can seek timely diagnosis and appropriate management to improve their quality of life. If you suspect you may have hypothyroidism or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. With proper management, many people with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Also Read: Mastering Bodyweight Exercises: A Comprehensive Guide to Achieving Fitness Goals